GIẢI BÀI 5 TUYỂN SINH LỚP 10 MÔN TOÁN NĂM 2022 CỦA TỈNH NGHỆ AN
- 20/06/2022
- 413 lượt xem
| Giải phương trình $$\sqrt{x^2+1}+3=\left(\dfrac{1}{x}-3\right)\left(\sqrt{9x^2-6x+2}+3\right)\quad (1)$$ |
Điều kiện: $\dfrac{1}{x}-3>0 \Leftrightarrow \dfrac{1-3x}{x}>0 \Leftrightarrow 0<x<\dfrac13$.
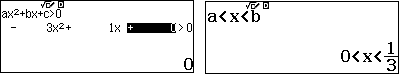
Phương trình có thể được viết $$x\left(\sqrt{x^2+1}+3\right)=(1-3x)\left(\sqrt{9x^2-6x+2}+3\right)$$
Đặt $u=1-3x$, ta thấy $u>0$ và phương trình trở thành $$x\left(\sqrt{x^2+1}+3\right)=u\left(\sqrt{u^2+1}+3\right)$$
$$\Leftrightarrow \sqrt{x^4+x^2}-\sqrt{u^4+u^2}+3(x-u)=0$$
$$\Leftrightarrow \dfrac{x^4-u^4+x^2-u^2}{\sqrt{x^4+x^2}+\sqrt{u^4+u^2}}+3(x-u)=0$$
$$\Leftrightarrow (x-u)\underbrace{\left[\dfrac{(x+u)(x^2+u^2+1)}{\sqrt{x^4+x^2}+\sqrt{u^4+u^2}}+3\right]}_{>0}=0\quad (2)$$
Ta có nhận xét rằng vì $x$ và $u$ đều dương nên phần trong móc vuông là dương. Do đó $$(2)\Leftrightarrow x-u=0\Leftrightarrow 4x-1=0 \Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac14$$
![]()
Về phương diện MTCT ta có thể test nghiệm duy nhất $x=\dfrac14$ như sau: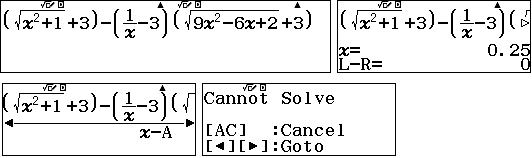 |
 BITEXEDU Chuyên trang chia sẻ tài liệu, kinh nghiệm ứng dụng giải toán trên máy tính cầm tay
BITEXEDU Chuyên trang chia sẻ tài liệu, kinh nghiệm ứng dụng giải toán trên máy tính cầm tay